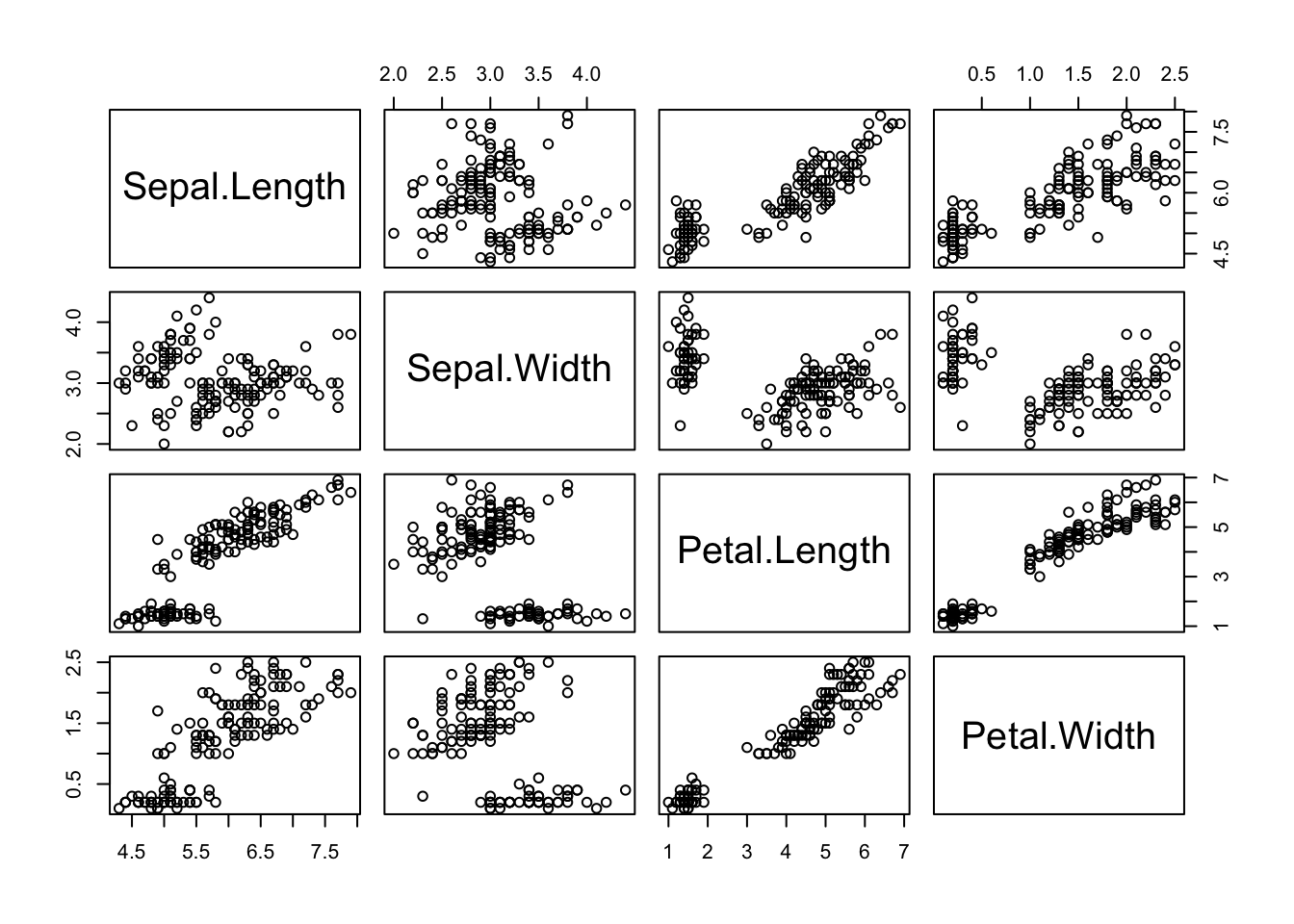
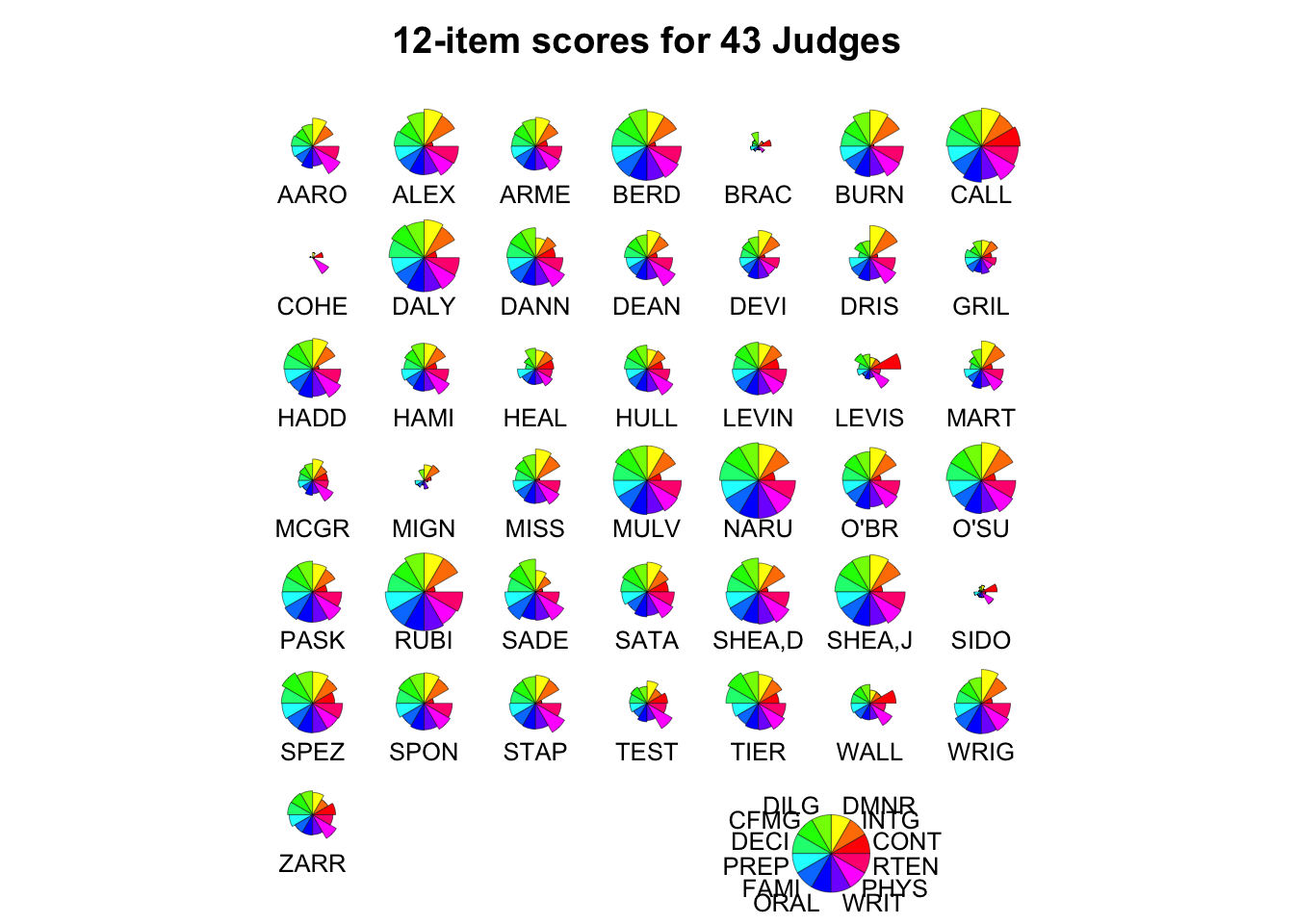
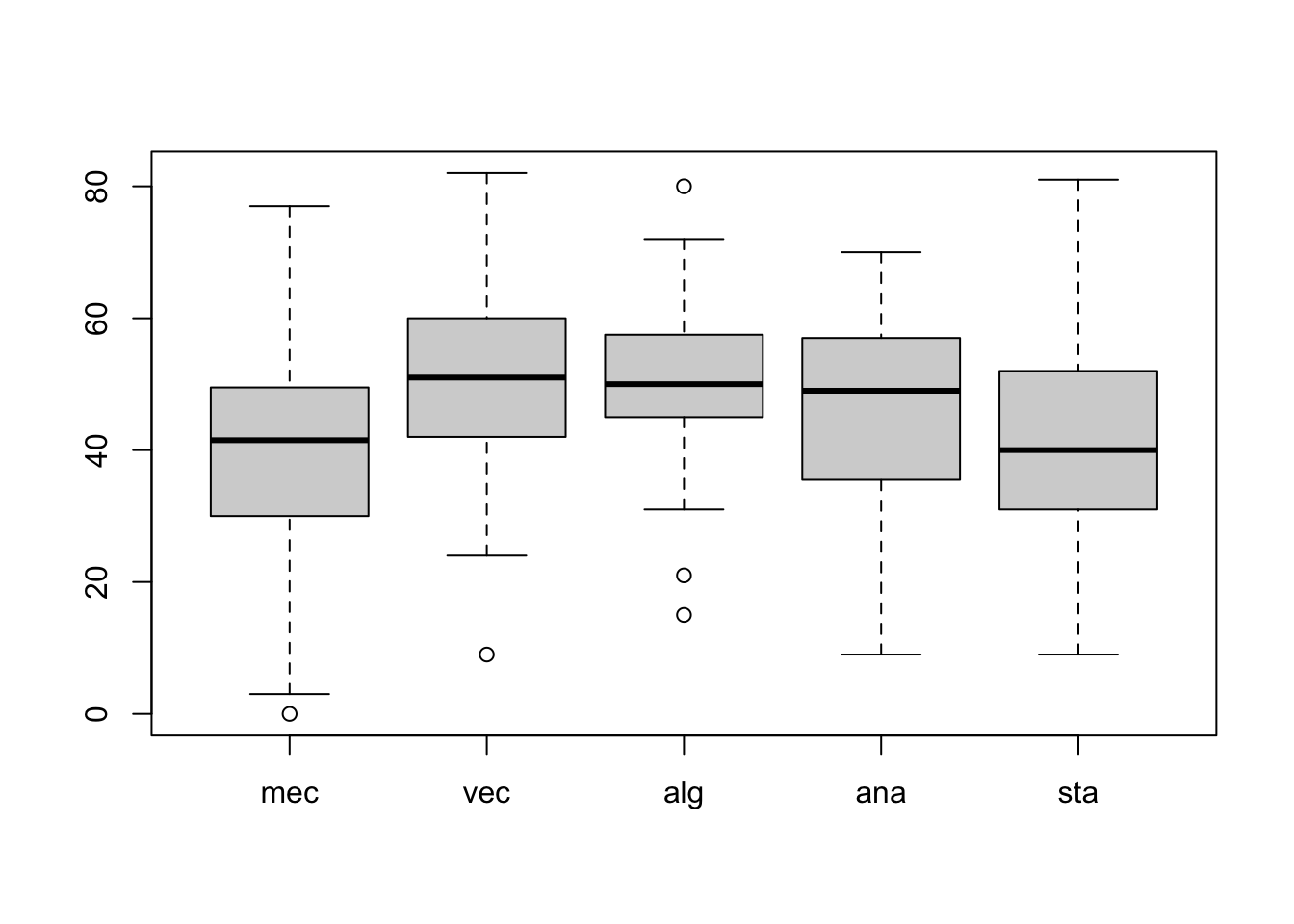
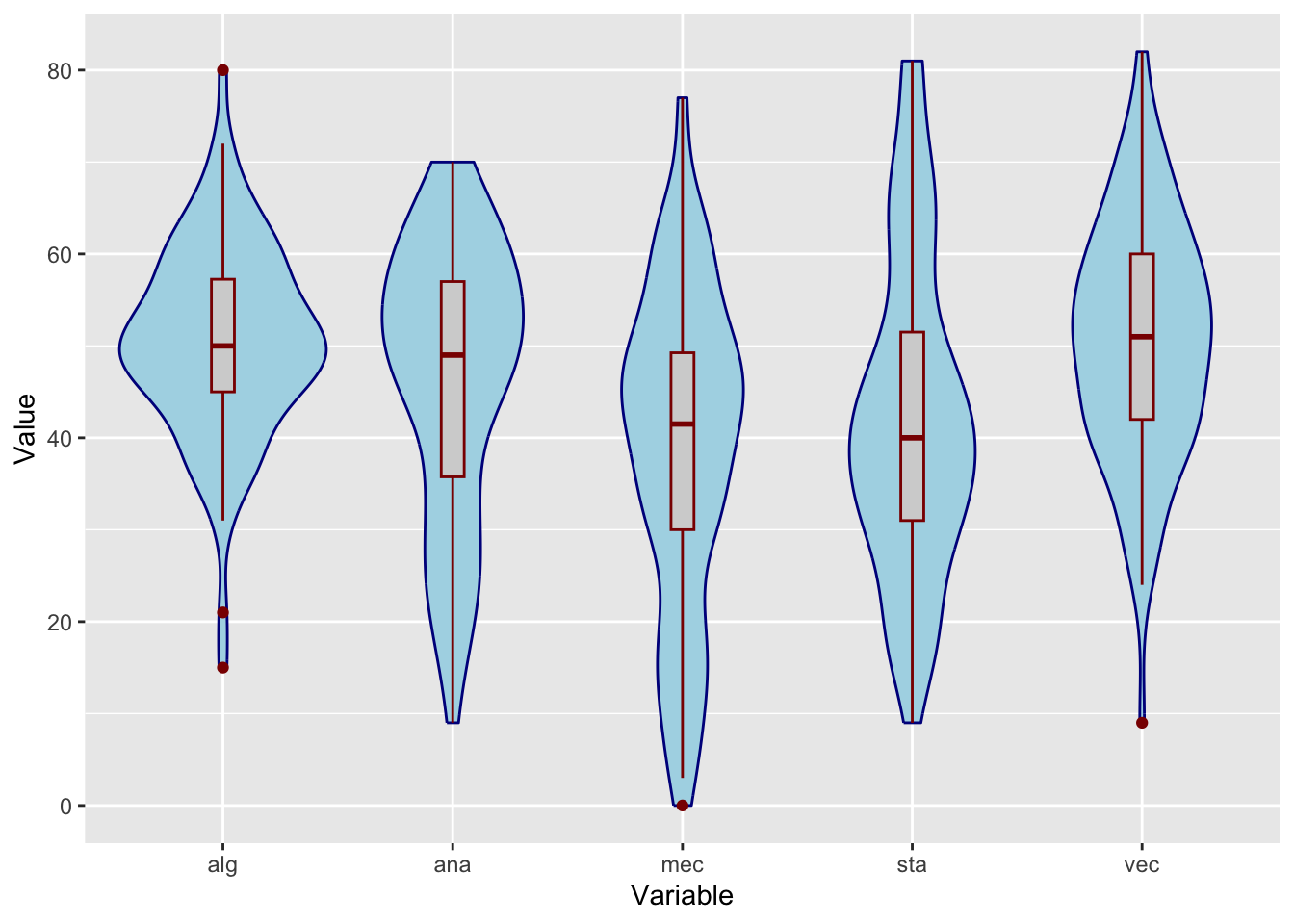
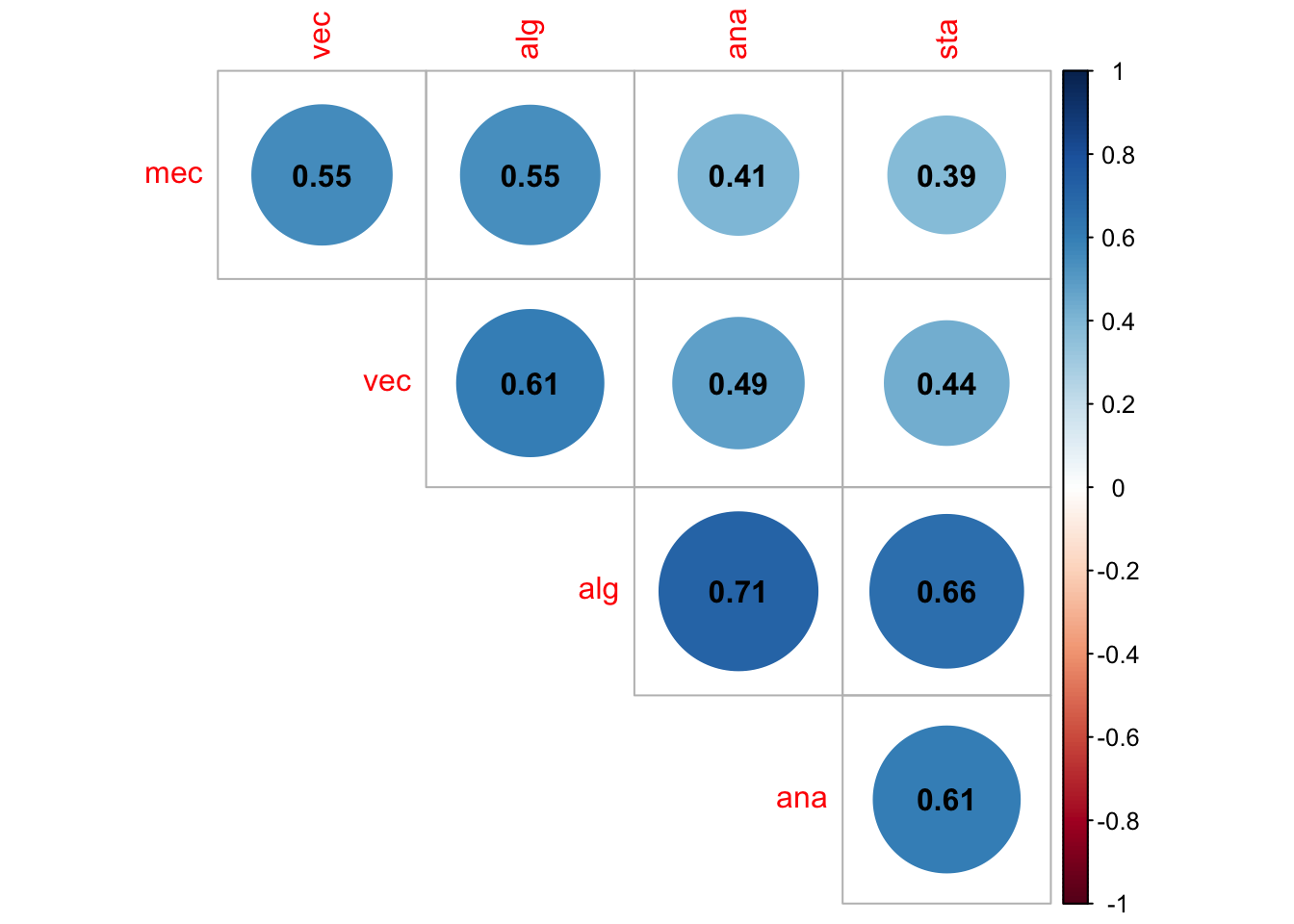
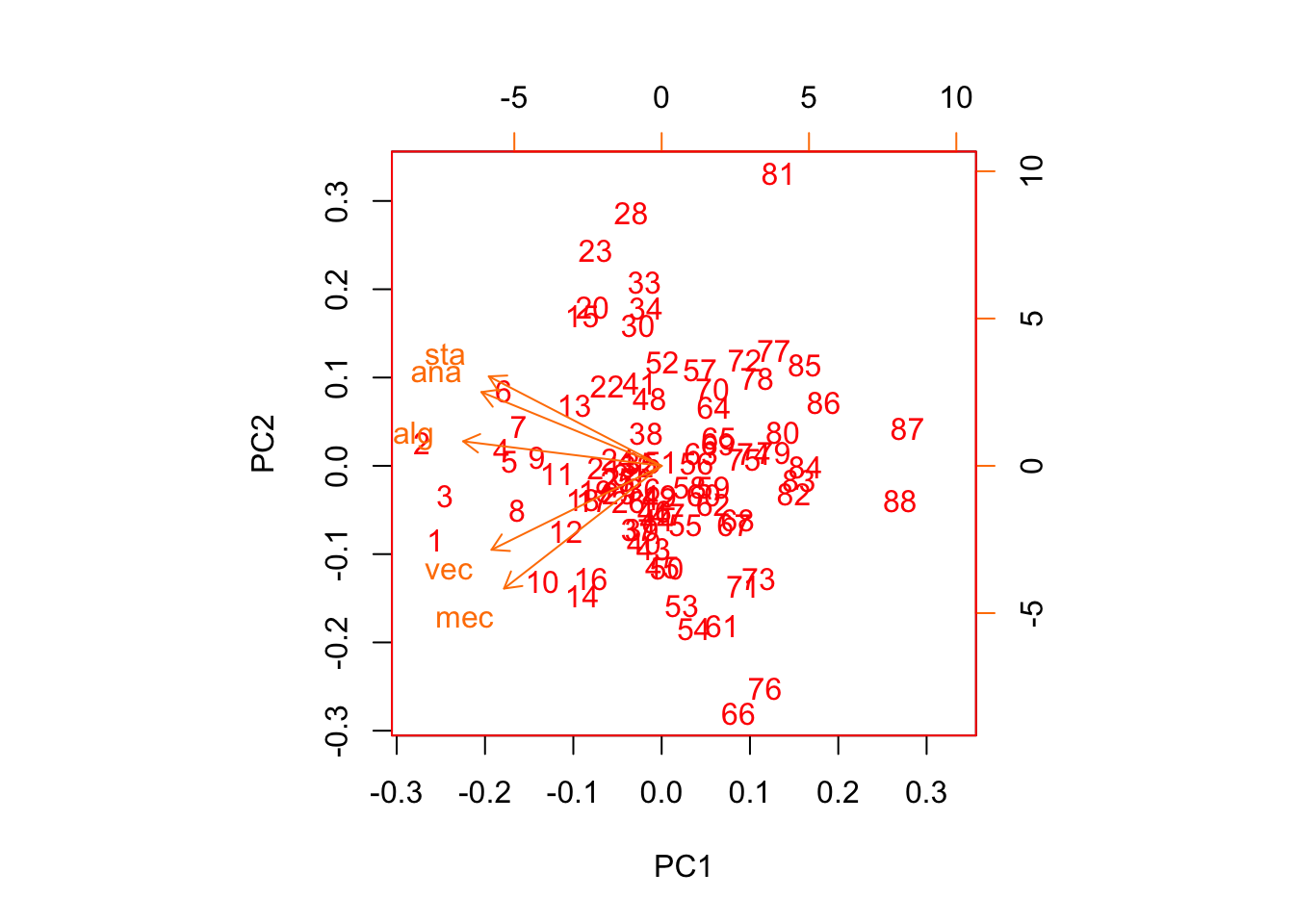
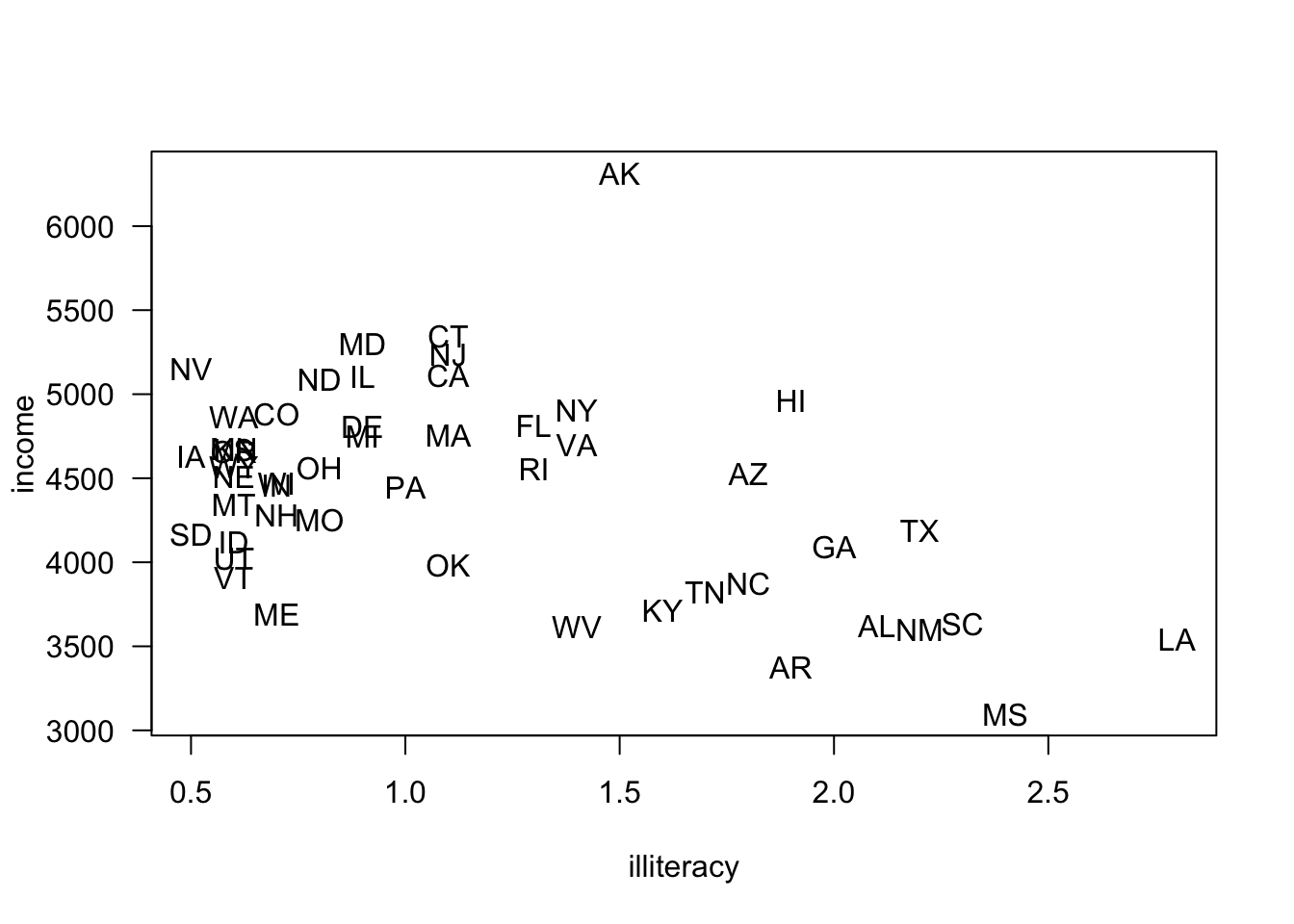
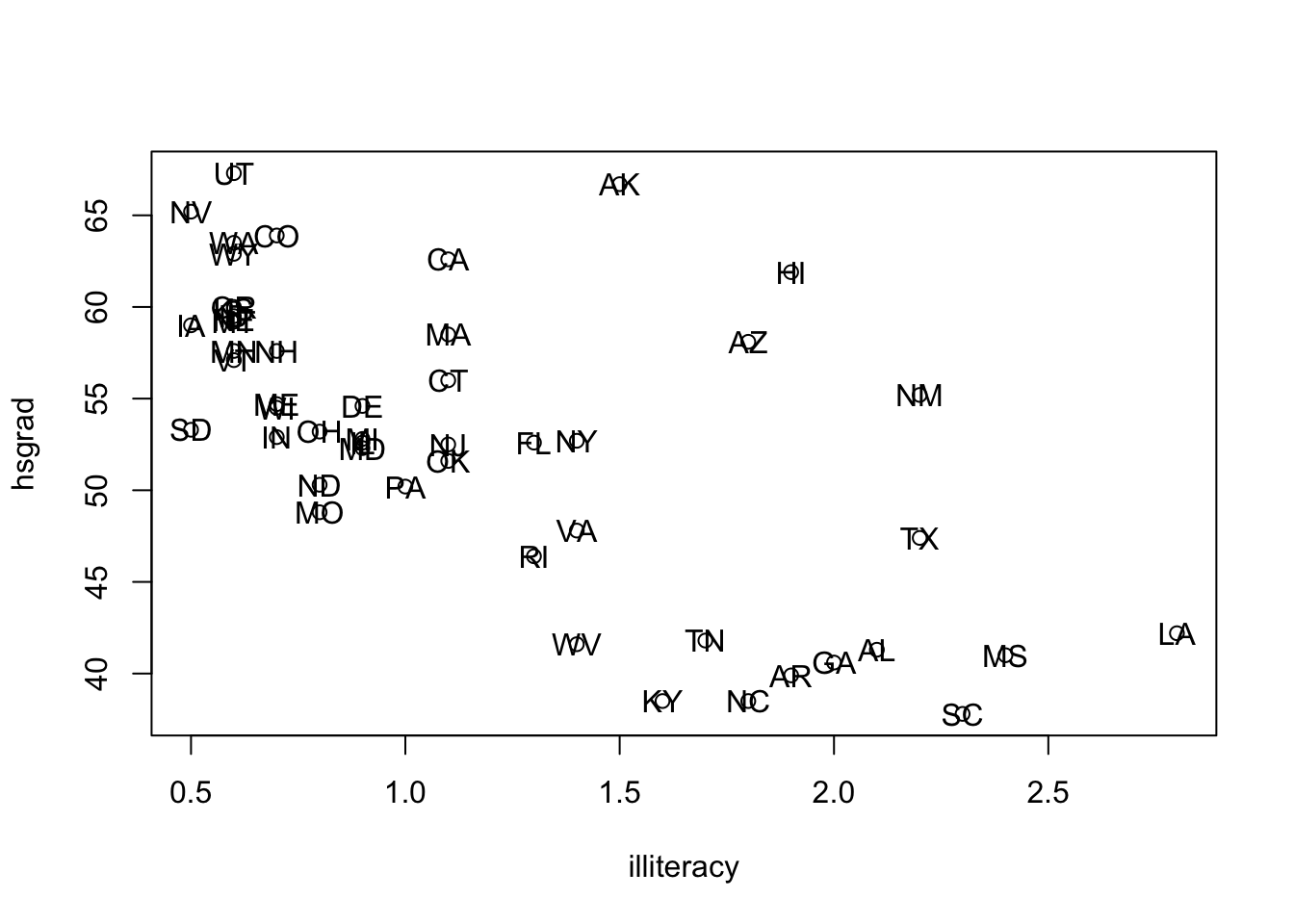
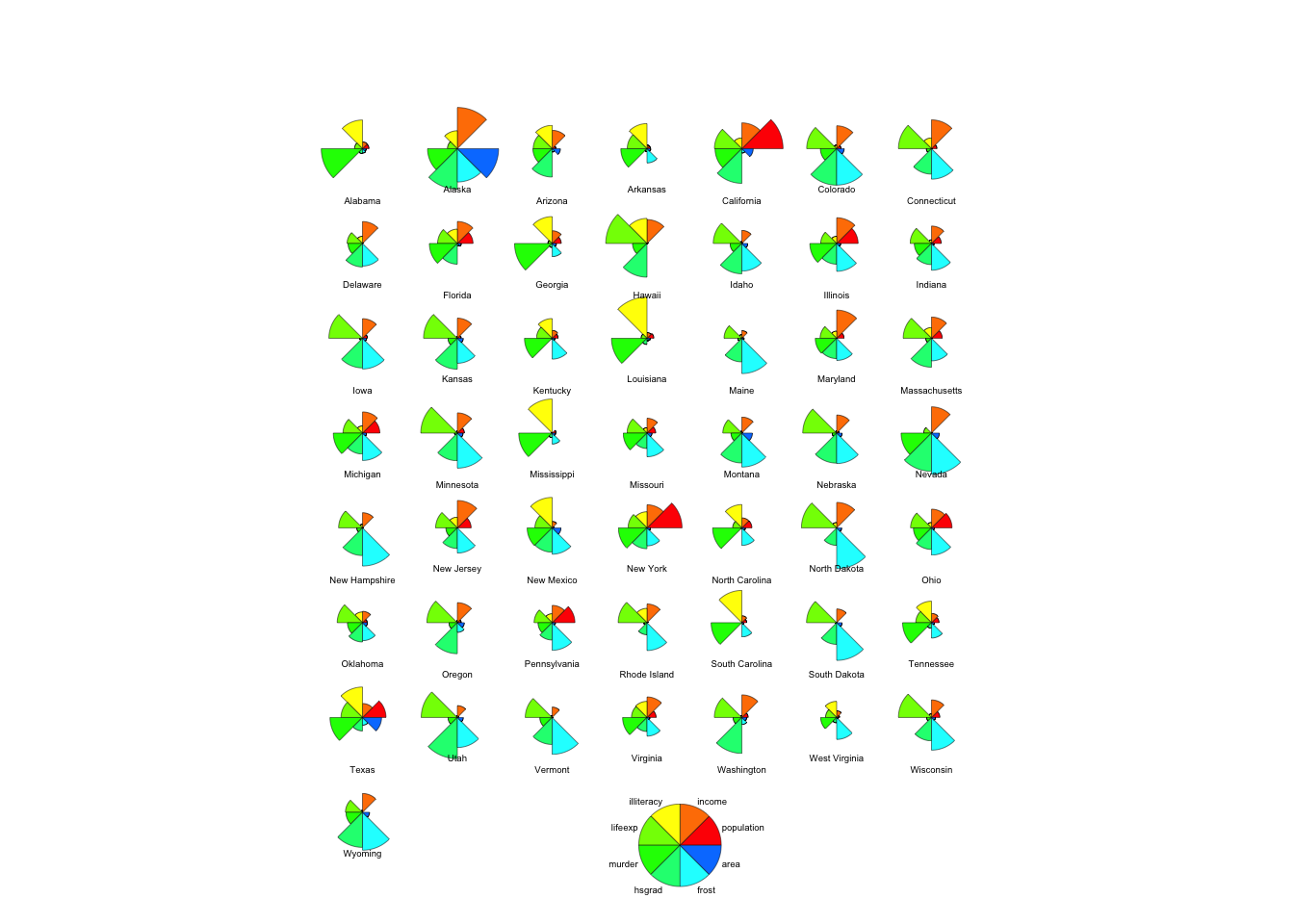
data(iris)
dim(iris)[1] 150 5summary(iris) Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width
Min. :4.300 Min. :2.000 Min. :1.000 Min. :0.100
1st Qu.:5.100 1st Qu.:2.800 1st Qu.:1.600 1st Qu.:0.300
Median :5.800 Median :3.000 Median :4.350 Median :1.300
Mean :5.843 Mean :3.057 Mean :3.758 Mean :1.199
3rd Qu.:6.400 3rd Qu.:3.300 3rd Qu.:5.100 3rd Qu.:1.800
Max. :7.900 Max. :4.400 Max. :6.900 Max. :2.500
Species
setosa :50
versicolor:50
virginica :50
# Shows pairwise scatter plots without outliers
pairs(iris[, 1:4])